Supernetting
Supernetting Definition
Supernetting is a routing technique that combines multiple neighboring IP networks into a single larger network route. It’s often also known as route aggregation or route summarization. Instead of listing many small networks separately, a router can group them together and advertise a single summary route. This reduces the number of entries in a routing table and makes larger networks easier to manage.
How Supernetting Works
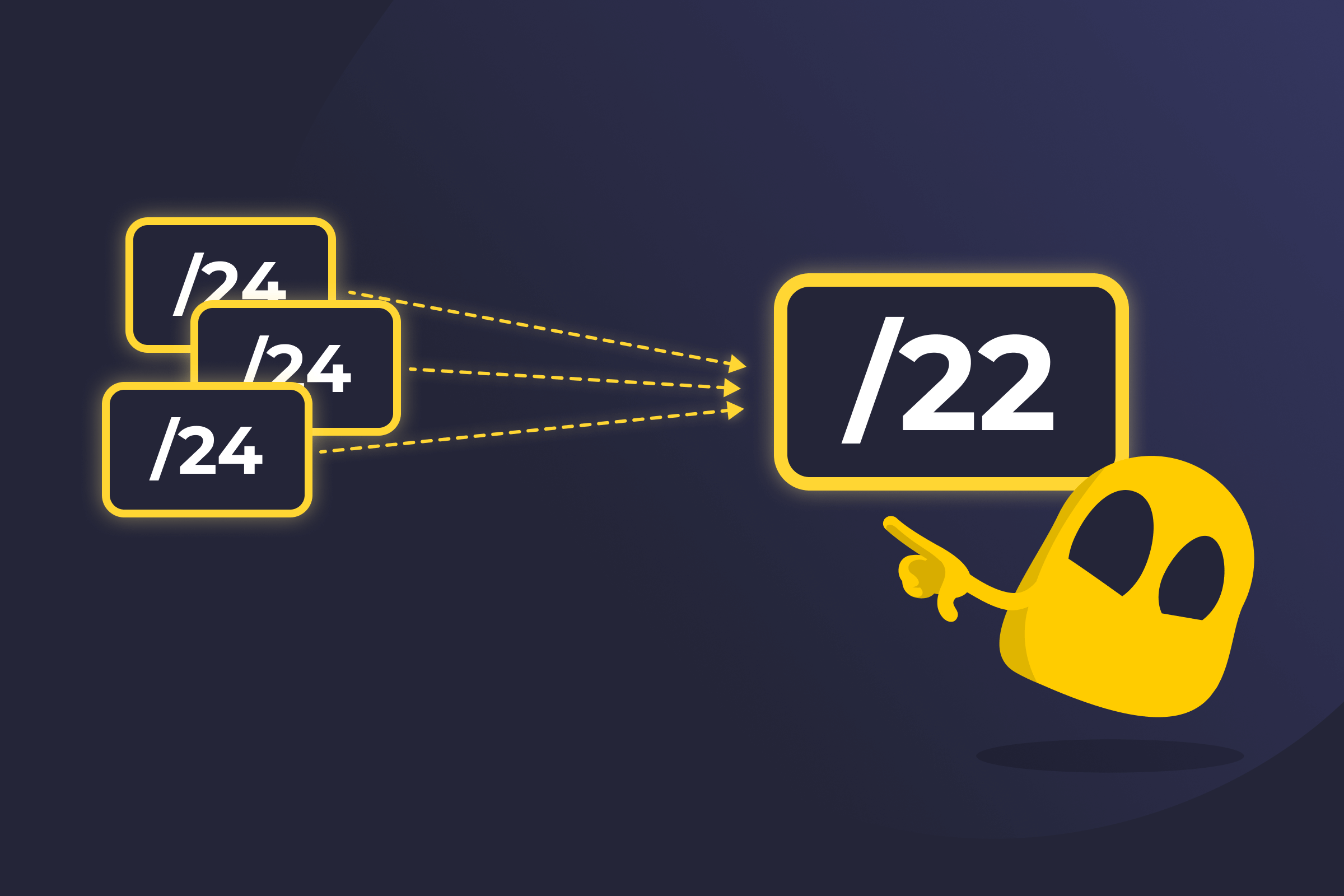
Supernetting works by grouping smaller networks that sit next to each other into one larger route, using CIDR notation. CIDR, or Classless Inter-Domain Routing, uses prefix lengths such as /24 or /22 to define how large a network is. The prefix tells routers how much of the IP address represents the network portion.
For this to work, the networks must be contiguous, with no gaps between their address ranges. They must also align correctly with the CIDR prefix boundary. When those conditions are met, several smaller networks can be represented as one larger prefix.
For example, four consecutive /24 networks can be summarized into a single /22 network if their address ranges are properly aligned. Instead of advertising four separate routes, the router advertises one aggregated route that covers them all.
Routers use a rule called "longest-prefix match" when deciding where to send traffic. If both a summarized route and a more specific route exist, the router chooses the more specific one. This ensures that detailed routing still works correctly even when supernetting is in place.
Common Use Cases of Supernetting
- Internal routing protocols: Protocols like OSPF use summarization to reduce routing updates between areas.
- Routing table optimization: Large backbone networks use route aggregation to prevent the global routing table from growing too large.
- ISP address management: Service providers group customer networks into larger blocks to reduce administrative overhead.
- Large multi-site networks: Companies with several locations summarize internal routes to simplify communication between offices.
- Enterprise networks: Supernetting reduces the number of routes routers must store and process.
- Site-to-site VPNs: Summary routes reduce the number of prefixes exchanged between connected networks.
Common Mistakes and Limits of Supernetting
- Grouping networks that aren’t adjacent: If address ranges don’t sit directly next to each other, the summary route won’t accurately represent them.
- Using the wrong prefix size: A miscalculated CIDR prefix can include addresses that don’t belong in the summary.
- Merging routes that exit through different paths: Combining networks with different next-hops can hide important routing differences.
- Creating overlapping supernets: Overlapping prefixes can lead to unexpected routing behavior and make troubleshooting more difficult.
- Oversimplifying network visibility: Large summary routes can make it harder to quickly see which specific subnet is involved in an issue.
Read More
FAQ
Subnetting divides a single network into smaller subnets to organize addressing and manage traffic. Supernetting combines multiple contiguous networks into one larger routing prefix to reduce routing table entries and simplify route advertisement.
Supernetting changes route advertisement and route aggregation, not security enforcement. Controls such as firewall rules, ACLs, segmentation, and monitoring still operate on the underlying subnets and hosts. If a summarized prefix is too broad, it can reduce visibility during audits, but it doesn’t add protection by itself.
Supernetting applies to both IPv4 and IPv6 because both use CIDR prefixes. A summary route can represent multiple contiguous subnet ranges when the prefix boundary is correct. The same routing logic applies, including longest-prefix match, which prefers a more specific subnet route over a broader supernet.

 45-Day Money-Back Guarantee
45-Day Money-Back Guarantee