Network Port
Network Port Definition
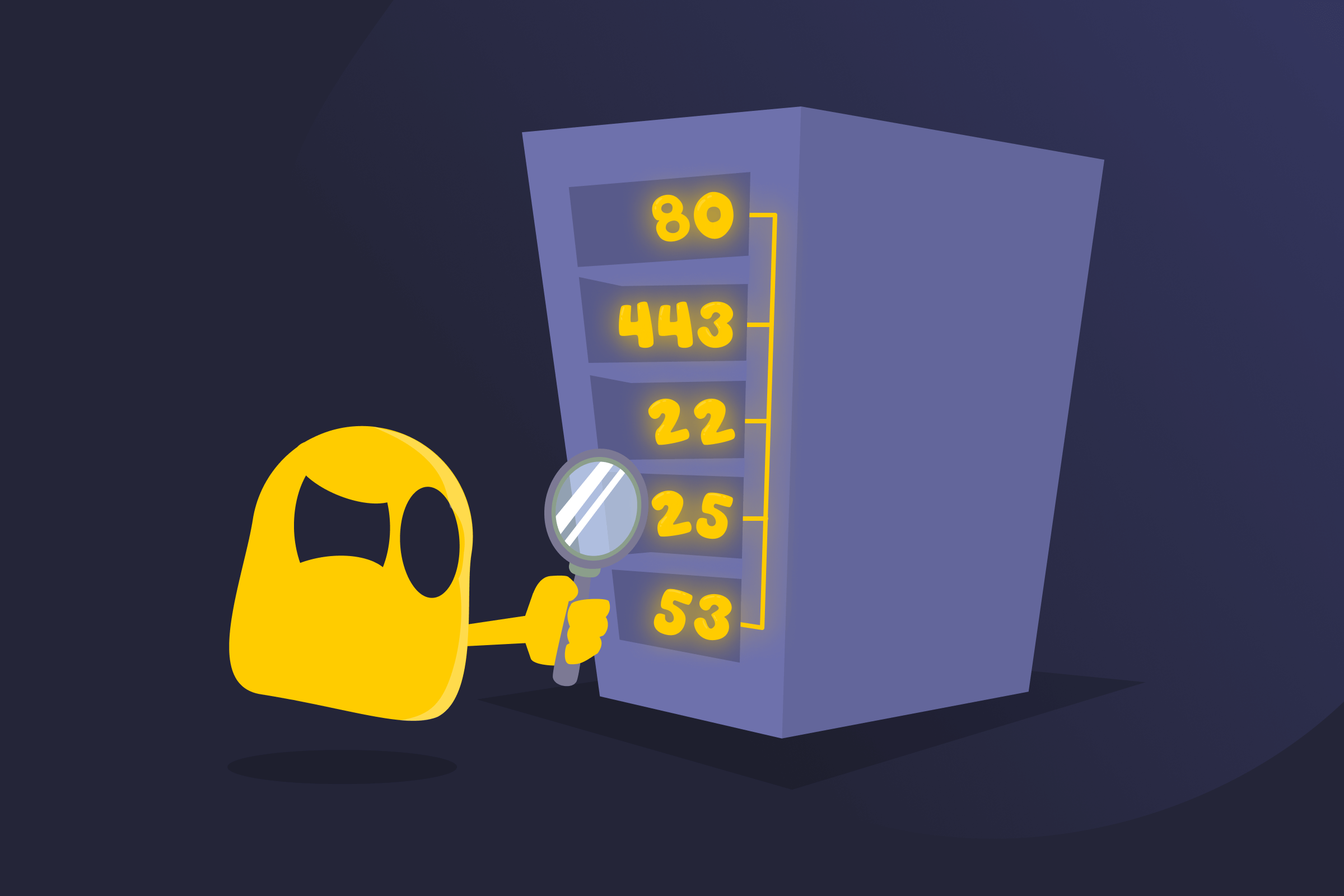
A network port is a virtual connection point that lets devices send and receive data across a network. Each port has a number that links it to a specific network service. For example, web traffic typically uses port 80 (HTTP) or 443 (HTTPS), while email services may use ports like 25 (SMTP) or 143 (IMAP). Ports make it possible for multiple applications to share the same network connection at the same time.
How Network Ports Work
When a device connects to the internet, its IP address marks its location on the network. Ports split that connection into smaller channels, each with a number that indicates which service or application the data belongs to.
When an app sends data, the operating system attaches both the IP address and the port number. This pair, called a socket, directs the data to the right place. Incoming traffic uses the same details to reach the correct app.
Since each port represents a specific service, they help organize communication on a device and keep multiple network activities running simultaneously. Firewalls also use port numbers to allow or block specific traffic, which makes ports important for security and troubleshooting.
Types of Network Ports
By Protocol
- TCP ports: Provide reliable communication and ensure data arrives in order.
- UDP ports: Offer faster communication and skip delivery checks.
By Range
- Well-known ports (0–1023): Host usual services such as HTTP (80) and HTTPS (443).
- Registered ports (1024–49151): Support specific apps or services like Microsoft SQL Server (1433).
- Dynamic or private ports (49152–65535): Manage temporary, client-side connections, like web browsing sessions.
Examples of Network Ports
| Port Number | Protocol | Full Port Name | Main Use |
| 20/21 | FTP | File Transfer Protocol | Transfer files |
| 22 | SSH | Secure Shell | Secure remote access |
| 25 | SMTP | Simple Mail Transfer Protocol | Send emails |
| 53 | DNS | Domain Name System | Resolve domain names |
| 80 | HTTP | Hypertext Transfer Protocol | Load web pages |
| 110 | POP3 | Post Office Protocol | Retrieve emails |
| 123 | NTP | Network Time Protocol | Sync clocks |
| 143 | IMAP | Internet Message Access Protocol | Handle emails |
| 443 | HTTPS | Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure | Load secure pages |
| 3389 | RDP | Remote Desktop Protocol | Remote desktop access |
Read More
FAQ
There are 65,535 ports available on a network. Each port is numbered from 0 to 65,535. These ports are grouped into well-known, registered, and dynamic ranges. Each range supports different types of network communication.
Yes, network ports can be opened or closed based on how a device or network is set up. Open ports accept incoming connections, while closed ports block them. Firewalls and security tools control which ports stay open in order to regulate access and block unwanted traffic.
Users can check open ports with built-in system tools. On Windows, the netstat command shows active connections and open ports. On macOS or Linux, users can run lsof -i or netstat -tuln. Many network scanners and security apps can also list open ports automatically.

 45-Day Money-Back Guarantee
45-Day Money-Back Guarantee