Full tunnel VPNs route all your traffic through the VPN tunnel by default, giving you maximum security. Split tunnel VPNs let you choose which apps or sites go through the VPN and which ones don’t, giving you flexibility. Choosing between the two options comes down to your needs. Let’s go through how split tunneling and full tunneling work, when to use each one, and how to set them up with CyberGhost VPN.
What Is a VPN Tunnel?
A VPN tunnel is an encrypted pathway your internet traffic travels through when you connect to a VPN. It keeps your online activity hidden from anyone who might be trying to monitor it. Even if someone managed to intercept your connection, they wouldn’t be able to decipher your data.
The tunnel also changes how your data gets to where it’s going. Instead of heading directly to the internet, your traffic is sent through a private VPN server first. This process masks your real IP address with one from your chosen server, which makes it harder to link your online activity back to you. All VPNs use some form of tunneling to protect your connection, but they don’t all offer split tunneling.
Split Tunnel vs Full Tunnel VPN: Key Differences

What Is Split Tunneling?
Split tunneling lets you choose specific apps or websites to use a VPN, instead of encrypting and rerouting all of your internet traffic. This is helpful if you want to keep certain activities private while using your real IP address for local services, like the weather app or food delivery.
Apps left outside the VPN can run at your normal connection speed, without the small slowdown encryption and re-routing can sometimes add. For example, you could keep your browser traffic in the tunnel to pay securely for a new game on public Wi-Fi, while routing the actual gameplay outside the tunnel to maintain better speed and lower latency. Letting some of your traffic use your regular connection also frees up bandwidth inside the VPN tunnel, letting it work faster, too.
Split tunneling is equally helpful for work setups that only need partial protection, where a part of the traffic goes through the VPN. Remote employees get secure access to company resources without routing all their personal traffic through the business’ private network. In-office workers can also use split tunneling to connect to a company VPN while still being able to use local utilities like department printers.
The downside is that split tunneling requires configuration and attention. You have to choose which traffic goes through the VPN and update the list as your needs change. Everything you do online isn’t automatically protected either, as traffic outside the VPN tunnel isn’t encrypted and uses your real IP address. On an unsecured public hotspot, for example, this could expose your identity and activity to anyone trying to monitor the network.
Lastly, you can’t split tunnel on every device. For example, iOS’s sandboxing security feature stops apps from interacting. This is designed to prevent malware from spying on other apps or buggy programs from taking down the whole system. But it also prevents VPNs from controlling other app traffic.
Pros of Split Tunneling
- Provides the flexibility to choose which sites or apps use the VPN’s IP address.
- Lets you control what stays protected.
- Preserves regular internet speed for non-VPN traffic.
- Keeps access to local sites like online banking or local network services like printers.
Cons of Split Tunneling
- Encrypts only selected traffic, exposing the rest to data leaks.
- Displays your real IP address for traffic outside the VPN.
- Requires the extra setup of choosing which apps or sites to exclude.
- Lacks compatibility with all platforms.
What Is Full Tunneling?
Full tunneling routes all your internet traffic through the VPN, without any extra setup. Every app, website, and service on your device goes through the encrypted tunnel and uses the VPN’s IP address. This gives you more complete protection, so it’s especially useful when you’re handling sensitive data. It can also make unsecured Wi-Fi networks safer to use.
Because it provides maximum security, full tunneling is often the default mode in most VPN apps. It’s also widely used in regulated industries with strict data security practices, like finance, healthcare, and government.
The downside is that full tunneling can sometimes affect your connection speeds. Encryption adds extra processing, and routing all your traffic through a VPN server can increase latency since your data has farther to travel. That said, any speed drops should be unnoticeable if you’re using full tunneling on a fast VPN.
Pros of Full Tunneling
- Encrypts all traffic automatically.
- Masks your real IP address on every site or service.
- Provides stronger protection for sensitive data.
- Makes connecting to public Wi-Fi and high-risk networks safer.
- Works right away, with no complicated setup.
Cons of Full Tunneling
- May slow down your connection.
- Might block your access to local services if you get an IP from a different location.
- Lacks flexibility; you can’t control traffic app-by-app.
Which Is More Secure: Split or Full Tunnel?
Full tunneling is more secure because it encrypts all the traffic leaving your device, including your browsing activity, messages, downloads, and app data. It’s the better choice when you need complete privacy, like accessing very sensitive data on an unsecured network.
With split tunneling, some traffic stays unencrypted and shows your real IP address. That can be fine if you’re running low-risk activities like streaming outside of the VPN connection to maintain fast speeds. But it can lead to accidental data leaks if you forget you’re not fully protected.
CyberGhost VPN gives you both options, so you can switch between split tunneling and full tunneling based on what you’re doing. On Android, you can choose which apps go through the VPN. On Windows, you can use the Exceptions feature to stop selected websites from using the VPN instead.
How to Use Split Tunneling and Full Tunneling with CyberGhost VPN
On Windows
- Open the CyberGhost VPN app.
- Click Smart Rules in the bottom left-hand corner, then open Exceptions.
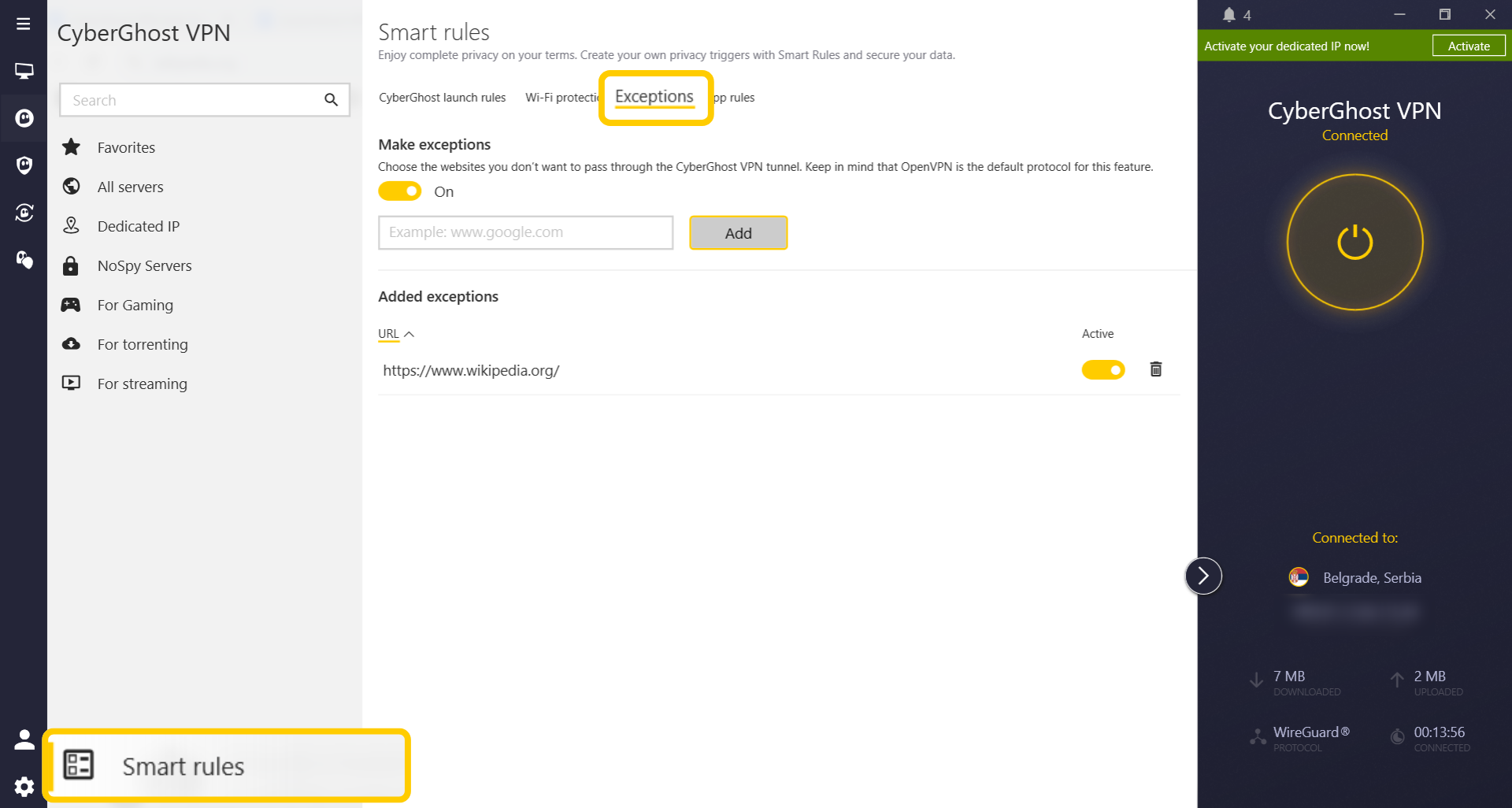
- Turn on the toggle switch under Make exceptions. Then, type in the URL of any website you want to exclude from the VPN tunnel and select Add.
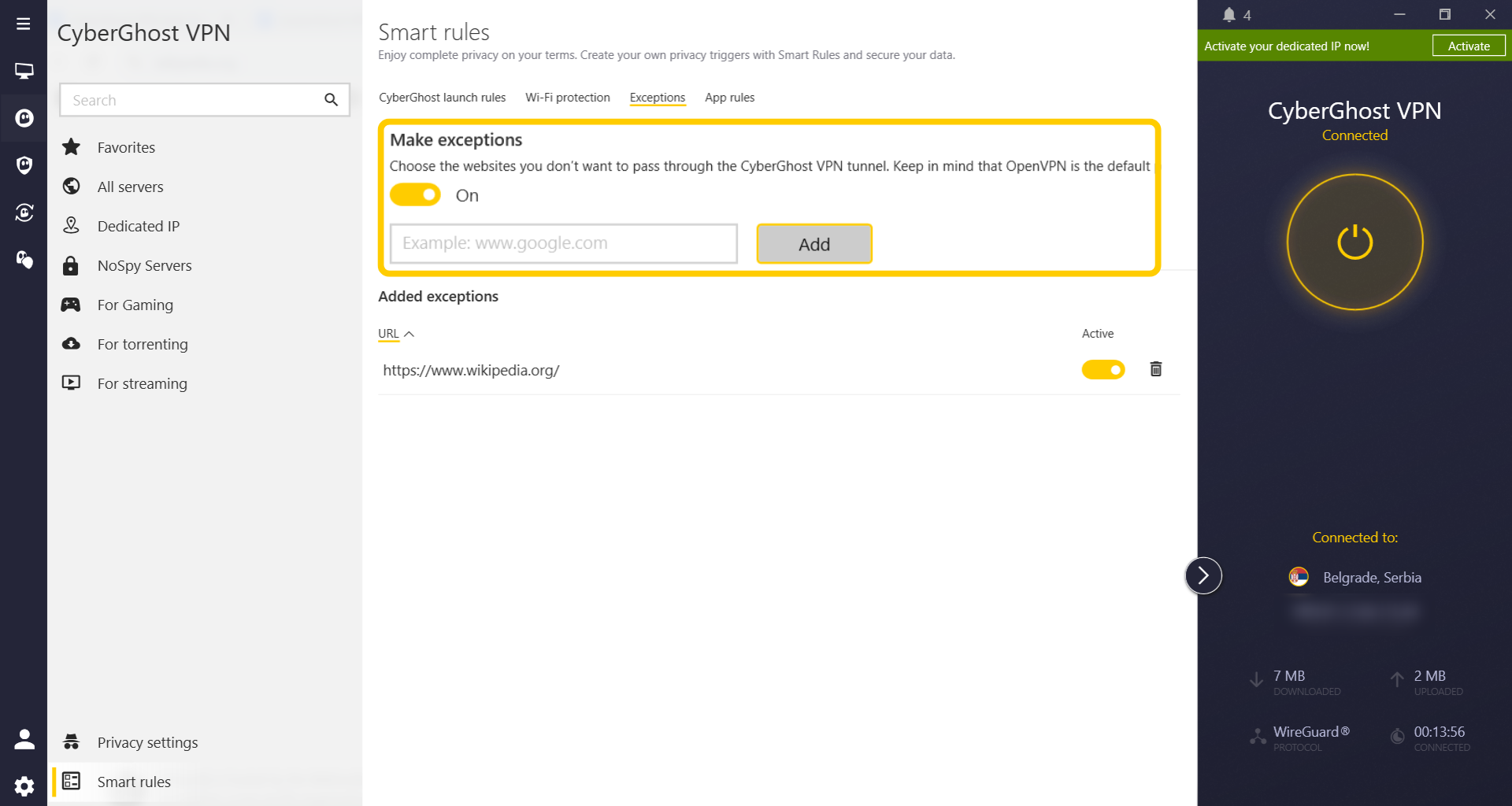
- To switch back to full tunneling, go back to Exceptions and remove all sites from your list.
On Android
- Open the CyberGhost VPN app.
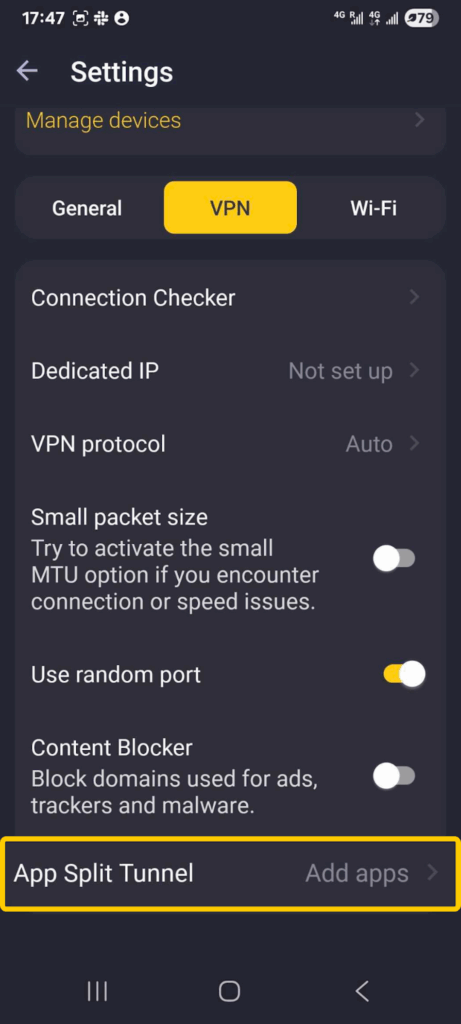
- Click on the cog icon to open your settings, then select VPN.
- Under your VPN settings, look for App Split Tunnel and press Add apps.
- Choose which apps should bypass the VPN.
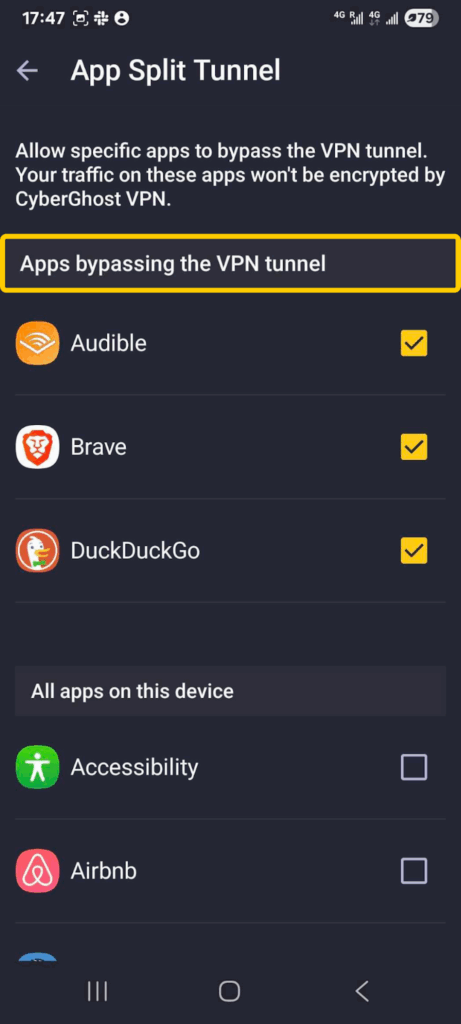
- To switch back to full tunneling, return to Add apps and turn off the toggle for all apps.
Choose the Tunnel That’s Right for You
The best tunnel depends on what you’re doing online. Split tunneling gives you more control. It’s ideal when you want to protect certain activities while still using other sites and apps with your local IP address and normal connection speeds. Full tunneling keeps things simple. It routes all your traffic through the VPN, so everything is encrypted by default. That makes it the better choice when privacy is your priority.
It helps to have a VPN that lets you switch between the two. CyberGhost VPN supports both split tunneling and full tunneling on Windows and Android. You also get a 45-day money-back guarantee, giving you plenty of time to test out each option and see which one works for you.
FAQ
What’s the difference between split tunnelling and full tunnelling in a VPN?
A full tunnel routes all your internet traffic through the VPN, so everything is encrypted and hidden from snoops. A split tunnel lets you choose which apps or websites go through the VPN and which use your regular connection. This means you can use your local IP address and the VPN server’s IP address at the same time for different activities. The downside is that split tunneling only protects part of your connection.
When should I use split tunneling instead of full tunneling?
Use split tunneling when you want to protect some activity but keep the rest on your normal connection. For example, if you want to browse privately with the VPN but stream with your usual internet speeds.
Is a full-tunnel VPN more secure than a split-tunnel VPN?
Yes. Full tunneling encrypts all the traffic from your device, so nothing is exposed. It’s the best option on public Wi-Fi or when you’re doing private tasks like working remotely or accessing sensitive files. Split tunneling only protects the traffic you include, which leaves some data unencrypted.
Can I choose which apps use the VPN with split tunneling?
Yes, if your VPN supports it. With CyberGhost VPN on Android, you can set some apps to run outside the VPN tunnel. This means you can route your banking app through the VPN to check it safely on public Wi-Fi, while letting a streaming app use your regular connection. On the Windows CyberGhost VPN app, you can also select specific websites to bypass the VPN.
Do all VPN providers offer split tunneling as a feature?
No. Split tunneling isn’t available with every VPN. CyberGhost VPN supports split tunneling on Windows and Android, giving you more control over how your traffic is routed.


Leave a comment