Your game freezes right before you score. Your video call with your boss turns into a slideshow. Connection issues like these are often at the heart of the Ethernet vs Wi-Fi debate. Both get you online, but they trade different strengths. Ethernet delivers steady, reliable performance, while Wi-Fi offers convenience and coverage.
The key is knowing which suits your needs in different situations. To figure that out, we’ll show you how Ethernet and Wi-Fi compare in speed, stability, security, and convenience. Depending on whether you’re playing games, streaming, working from home, or just browsing, you’ll find out which one is a better fit.
What’s the Difference Between Ethernet and Wi-Fi?
Ethernet is a wired connection, using a network cable from your router to your device. The signal stays inside the cable, so it’s not affected by physical obstructions or interference from other electronics. This results in steady speeds and low, predictable latency, making it great for gaming, video calls, and 4K streaming. The trade-off is that you need a cable run and a free port on your router.
Wi-Fi is a wireless connection where your device communicates with the router via radio waves. This makes Wi-Fi connections incredibly flexible and well-suited for mobile devices. However, speeds can vary depending on distance, obstacles like walls and floors, and even interference from neighbors’ networks. This means Wi-Fi can be unpredictable and deliver fluctuating performance results.
Ethernet vs Wi-Fi: Key Factors to Consider
Ethernet is consistent, while Wi-Fi is convenient. Many homes use both by wiring a few devices to benefit from faster speeds while using Wi-Fi for other gadgets. To help you decide which option to use and when, let’s compare the two.

Speed
Ethernet delivers steady speeds because the signal stays inside the cable. A typical home setup uses Gigabit Ethernet (up to 1,000 Mbps), while many routers and PCs now support 2.5 Gbps or 10 Gbps. Those refer to the maximum possible speeds; you still need an internet provider that can deliver such ultra-fast speeds.
Wi-Fi can also be fast, especially if you have the latest-generation Wi-Fi router (produced in the last year or two). Today’s routers often support standards like Wi-Fi 6/6E/7, and they can deliver speeds from 9.6 Gbps (Wi-Fi 6/6E) up to 46 Gbps (Wi-Fi 7). However, everyday speeds are typically lower and less reliable than Ethernet, as they depend on factors like obstacles and distance from the router.
Learn more: How to Increase Your Internet Speed: Easy Tricks That Actually Work
Device Compatibility
Most modern devices work over Wi-Fi out of the box. That includes phones, tablets, laptops, Smart TVs, streaming sticks, smart speakers, and more. Some exceptions exist, like desktop PCs without a Wi-Fi card, older printers, and hard-wired professional gear. For everyday use, Wi-Fi is the default.
Ethernet is more limited by hardware, as it requires a physical port. You’ll find this port on many stationary devices, like desktop PCs, game consoles, network-attached storage, and set-top boxes. Many thin-and-light laptops, tablets, and all phones lack an Ethernet port, but you can add one with a USB-C/Thunderbolt adapter or docking station.
Stability and Latency
Ethernet isn’t affected by airwaves, which keeps latency low and steady. Since latency is the delay between sending a request and getting a response, the lower it is, the faster your data can travel. That’s why Ethernet is typically the go-to for competitive gamers and frequent video callers, as it can keep lag and connection drops to a minimum.
Wi-Fi shares radio space with your neighbors and household gadgets. This interference can cause speed drops and sudden latency spikes. You can improve this with a good router placement and switching between different bands by accessing your router’s admin panel (2.4 GHz, 5GHz, and 6 GHz). However, even with the most optimal router location, your ping most likely won’t be as low as it would be if you used Ethernet.
Security
To hack an Ethernet connection, an attacker usually needs physical access to tap into traffic, which can be the cable itself, a wall jack, switch port, or router. This makes traffic interception far less likely than with Wi-Fi, which broadcasts over radio and can be captured from outside your home. Ethernet isn’t immune to security issues, but the attack surface is smaller since there’s no over-the-air signal to harvest.
The gap widens on public Wi-Fi. You don’t control the hotspot, so you can’t verify how it’s configured or know who else is connected. Common risks include “evil twin” networks and traffic inspection by the hotspot operator. Local observers may see which sites you connect to, while an attacker might try to redirect you to a malicious website and collect any personal information you share.
A reliable VPN adds a layer of privacy to both Ethernet and Wi-Fi connections. It masks your IP address and scrambles your data, reducing what others can learn about your activity. You should also turn on your VPN’s kill switch so if the connection drops, your device will block all traffic until the connection is re-established. CyberGhost VPN includes strong encryption, data leak protection, and a kill switch to keep this protection consistent on wired and wireless networks.
Setup and Convenience
Ethernet needs a cable run and an available Ethernet port on your devices and router. It’s a set-and-forget solution once installed, since it needs no tweaking or manual setups. Wi-Fi is equally as simple to run, but it’s much more flexible. Most routers come with a predefined Wi-Fi network name and password, which you can use to access the network from any compatible device anywhere in your home.
Gaming and Streaming
For online or cloud gaming, Ethernet wins thanks to lower latency and faster speeds. When it comes to streaming, both options work well. A strong Wi-Fi signal handles 4K easily, unless your Wi-Fi is congested or the router is far away.
Real-World Scenarios: Which Connection Works Best?
Choosing between Ethernet and Wi-Fi isn’t about “right vs wrong.” It’s about the job you’re doing and where your devices are.
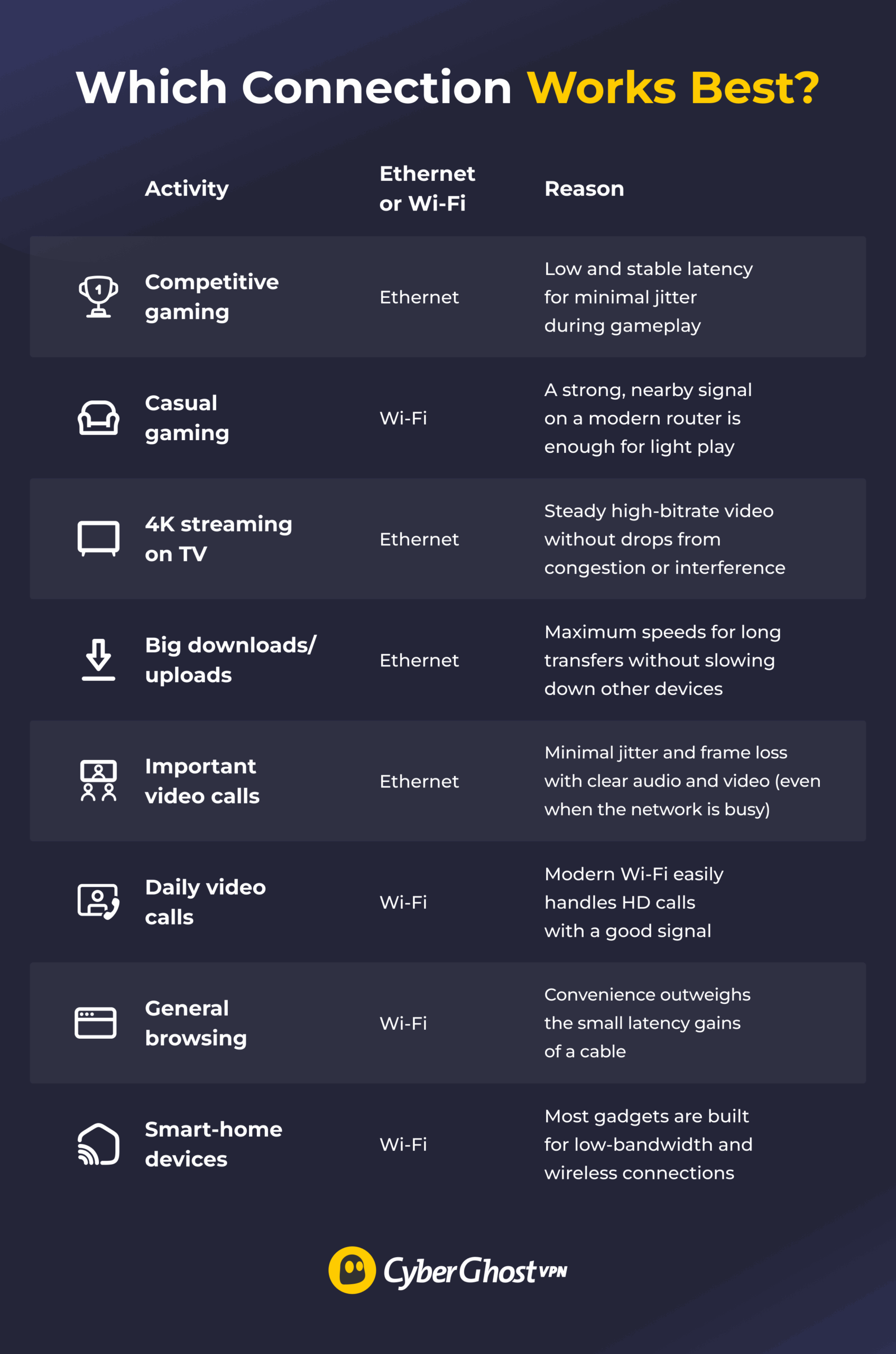
When Should You Use an Ethernet Connection?
-
- Competitive or online gaming: Ethernet offers the lowest and most consistent latency, reducing lag and minimizing spikes.
- 4K/8K streaming on a TV/console: A wired connection keeps your video quality stable and prevents constant buffering.
- Large downloads/uploads or cloud backups: Ethernet delivers consistent, high-speed data transfers, letting large files move quickly without interruptions.
- Hosting video calls or live streams: A wired line reduces dropouts and maintains smoother audio and video even during long sessions.
- Work from home: Ethernet supports fast and reliable access to files, remote desktops, and shared drives.
When Should You Use a Wi-Fi Connection?
-
- Everyday browsing, social, and shopping: Wi-Fi provides speeds fast enough for lightweight tasks, like browsing, without the hassle of using a wire.
- Connecting portable devices, like laptops and phones: Wireless connections let you stay online while moving freely around your space.
- Smart home devices: Most smart speakers, cameras, and IoT gadgets are designed for wireless connections and don’t have an Ethernet port.
- Streaming far from the router: Wi-Fi can offer more than enough bandwidth for HD or 4K streaming, as long as your signal is strong.
Can You Use Ethernet and Wi-Fi Together?
Most homes use Ethernet and Wi-Fi together. A simple rule of thumb is to use Ethernet on devices that stay put and Wi-Fi on devices that can be moved. Desktop PCs, consoles, and Smart TVs should use Ethernet, while phones and laptops benefit more from Wi-Fi. Keep in mind that, if both are connected, most systems will use the wired link over a wireless option.
How to Fix Common Ethernet and Wi-Fi Connection Issues
While more common with Wi-Fi, slow speeds and lag can creep in regardless of your setup. You don’t need to be a tech wiz to troubleshoot them though. Here’s how you can get more from Wi-Fi and Ethernet.
How to Fix Slow Wi-Fi
-
- Disconnect idle devices: Connected phones, tablets, gaming consoles, and smart gadgets eat up bandwidth even when you’re not using them.
- Restart your router: A simple reboot can often clear glitches and refresh your connection.
- Change your Wi-Fi channel: Nearby routers on the same channel can cause interference, but switching to a less crowded option can free up your signal.
- Keep your router up to date: Router updates patch bugs and vulnerabilities and improve speeds.
- Make your signal stronger: Place your router in a central, elevated place, away from walls, appliances, and electronics. If your home is big or has thick walls, consider adding mesh Wi-Fi units to help the signal travel further.
How to Fix Slow Ethernet
-
- Check your cables: Old or damaged cables can cap your speeds. Cat6 or Cat6a cables reliably support gigabit speeds (or higher), even over longer distances.
- Secure the connections: Loose plugs or poorly seated jacks can cause sudden speed or connection drops.
- Adjust your network adapter settings: Network adapters set to the wrong speed or duplex mode can bottleneck performance. “Auto-negotiate” allows devices to run at the best speed possible.
- Replace aging hardware: Outdated routers or switches may cap your speeds at 100 Mbps instead of allowing a full gigabit.
Choose Ethernet for Speed, Use Wi-Fi for Convenience
There’s no single “best” for everyone. If you need the fastest speeds your connection can reach, plug in. Ethernet is the best way to get the maximum connection speeds. That said, Wi-Fi delivers incredible flexibility with fewer cables. The smartest decision would be to mix the two, keeping your network fast and practical without a wiring project in every room.
Ethernet and Wi-Fi both give you access to the internet, but, on their own, they don’t guarantee safe and private browsing. CyberGhost VPN protects your data on wired and wireless networks with top-tier encryption, helps block trackers, and keeps your activity more private with a strict no-logs policy. This means it doesn’t track, store, or share your data while you’re connected. You can also count on a 45-day money-back guarantee, giving you enough time to test all features risk-free.
FAQ
What’s the main difference between Ethernet and Wi-Fi?
Ethernet connects devices to the network over a physical cable. You plug into the router directly, an Ethernet wall jack, or a network switch that links back to the router. Using an Ethernet cable gives you a direct and consistent connection with fewer slowdowns and drops. Wi-Fi is typically slower than Ethernet, but it doesn’t require cables, as it allows your devices to connect using radio waves. This means it can cover your entire household in one go.
Which is better for online gaming: Ethernet or Wi-Fi?
Ethernet is a better option for gaming than Wi-Fi, as it provides much lower latency and faster speeds. If you must use Wi-Fi, you can cut interference by using the 5 GHz/6 GHz band instead of 2.4 GHz or putting the router closer and higher, with as few walls and metal objects between it and your device. Another possibility is to pick a clear Wi-Fi channel (after doing a quick Wi-Fi scan using a mobile app) by accessing your router’s admin panel via a web browser.
Is Ethernet faster than Wi-Fi for downloading and streaming?
Often yes, especially for big downloads, because wired speeds are more consistent. For streaming, both wired and wireless connections work if your signal is strong. Keep in mind that FHD (1080p) streaming requires 5-10 Mbps, whereas 4K streaming requires a connection of 25 Mbps or higher.
Does using Ethernet reduce latency and ping compared to Wi-Fi?
Yes, Ethernet usually reduces latency and ping more than Wi-Fi. That’s because a cable isn’t affected by wireless interference, shaving milliseconds off ping. That might sound like a small difference, but it can be quite noticeable in competitive gaming and video calls.
Can Wi-Fi ever be as stable as a wired Ethernet connection?
Yes, it can come close under ideal conditions. To make that happen, you need a modern router, a short distance from it, a clear line of sight, and minimal interference. However, remember that radio signals are variable by nature. A cable remains the best option for stable connections.
What are the advantages of using Ethernet over Wi-Fi?
With Ethernet, you get lower latency, which is excellent for gaming and video calling. You also get more consistent speeds, crucial for downloads and uploads, and can avoid wireless interference from neighbors and household gadgets. From a security angle, a wired link doesn’t broadcast over the air, so a passerby can’t try to join your network from outside your home. Intercepting Ethernet requires physical access to a cable, wall jack, switch, or a compromised device on your LAN.
Are there any downsides to using Ethernet instead of Wi-Fi?
The biggest downside of Ethernet compared to Wi-Fi is that you’re tied to a cable. This limits where you can sit and use your device. Additionally, running cables through a home can be messy. Many mobile devices, like phones and tablets, also lack Ethernet ports, which means you have to connect them to Wi-Fi.
When is Wi-Fi more practical than Ethernet?
Wi-Fi is a more practical option when you’re using mobile devices and need to move around or work in different rooms. Also, it’s a much better option when you can’t run cables because you’re renting, using a shared space, or dealing with tricky house layouts.
Can I use both Ethernet and Wi-Fi at the same time?
Yes, most devices can connect to both. However, your device can use a single connection at a time, and it’ll always pick Ethernet over Wi-Fi. If you want to use Wi-Fi, unplug the cable. Otherwise, leave the cable in for your device to use an Ethernet connection.
How do I switch from Wi-Fi to Ethernet on my device?
To switch from Wi-Fi to Ethernet, plug an Ethernet cable into your device and connect it to a wall jack or directly to your router. Your device should automatically switch to a wired connection. To be 100% sure that your device uses Ethernet, you can also turn off Wi-Fi in your device’s network settings.


Leave a comment